Multi-Techno Integrated Solution
Table of Contents
ToggleTypes, Features, and Functions of ERP Modules
In the last few decades, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems have become important tools for companies. Important business tasks can be automated with an ERP system, which also stores all the financial and operational data from the whole company in one place. It gets this information from several modules that were made to help different areas, like accounting, supply chain, and human resources, do their jobs.
All employees can get the information they need from an ERP system to answer important questions about their department’s present performance, plans for the future, and areas that need to be improved. This one source of data ensures that everyone, no matter their role, is looking at the same numbers and reduces problems with data quality and consistency problems. It also helps people make better choices, which makes things run more smoothly and saves money. ERP can also automate many jobs, cutting down on mistakes and giving workers more time to do more strategic work.
Finance and accounting, purchasing, manufacturing, Inventory Management, order management, warehouse management, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), purchasing, and workforce management are all common ERP tools that help with both the back office and the front office. Professional services automation (service resource management), human resources management, e-commerce, and marketing automation may be part of more feature-packed systems.
What Are Modules in an ERP System?
Every ERP module is made to help with a certain business function. It gives employees the info and support they need to do their jobs. As the business adds more modules, the ERP System will still be the only source of correct data because all of them can connect to it. If the ERP system is the toolbox, then the modules are the screwdriver, wrench, hammer, and other tools that can be used for different tasks.
How can ERP modules help a company?
ERP can adapt to changing business needs because it has built-in modules. This is a big reason why this software is so popular. A business can only buy useful modules for its operations, business plan, and main problems. Then, as the business grows, it can add ERP tools to meet new needs or deal with contemporary issues.
Modular ERP Software is great because it lets a business add new features while keeping the core features the same. If the business picks a well-known ERP provider with many modules, it doesn’t have to go through the time-consuming process of setting up a new ERP system every time it needs to change.
What do ERP providers charge for each module?
There is a lot of variation in what modules come with an ERP buy and what modules cost extra. Most of the time, the base plan comes with the most important financial functions. Other features, like CRM and HR Management, may cost extra. If you’re a manufacturer, you might buy a package that includes supply chain management; if you’re a store, you might buy a package that provides for commerce. Software-as-a-service (SaaS) vendors charge by the user per month or per year. On-premises ERP vendors charge an upfront fee for each user registration. There are sometimes charges based on the deal.
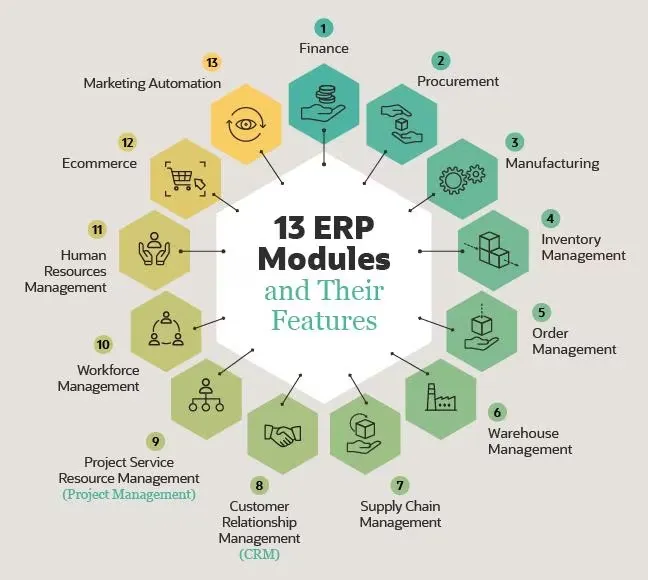
13 ERP Modules and What They Do
This picture shows the 13 parts of ERP and how they connect.
1. Money Matters
Finance and Accounting are the most important parts of ERP because they help businesses see how their money is doing now and what it will be like in the future. This module’s most important features are handling the general ledger and keeping track of accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR). It also makes and keeps important financial records, like tax returns, balance sheets, and payment papers.
The financial management module can automate billing, paying vendors, managing cash, and balancing accounts. This helps the accounting department close the books on time and follow the rules for recognizing revenue. It also has the information that people who work in financial planning and research need to make important reports, like profit and loss (P&L) statements, board reports, and scenario plans.
2. Buying Things / Procurement Module
The procurement module, also called the purchasing module, helps a business get the goods and supplies it needs to make and sell goods. In this module, companies can keep a list of approved vendors and link those vendors to specific things. This helps with managing relationships with suppliers. The program can automatically ask for quotes and then track and review the quotes that come in.When a business agrees to a price, the procurement module helps the buying group make and send out purchase orders. It can then keep track of that order as the seller turns it into a sales order and ships the goods, immediately updating the stock levels when the order comes.
3. Making Things
Material requirements planning (MRP) systems, the first form of ERP, were made for manufacturers. Manufacturing is still an important part of ERP. These days, most ERP systems come with a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) or production control system. The manufacturing module helps manufacturers plan their production and ensure they have all the raw materials and tools needed for scheduled production runs. During production, it can keep track of the status of goods-in-progress and help companies compare real output to what they had planned. It also shows what’s happening on the shop floor in real-time, keeping track of both work-in-progress and finished things. It can figure out how long it usually takes to make something and then compare that to what is expected to be needed to plan the right amount of production.
4. Management of Inventory
Inventory control is made possible by the Inventory Management Module, which keeps track of item amounts and locations down to the SKU level. Through an integration with the procurement tool, this module gives a full picture of both present and new inventory. This software helps companies keep track of their inventory prices and ensure they have enough stock without holding too much cash on hand. An inventory management app can compare sales trends to available products. This helps businesses make smart choices that improve profit margins and inventory turnover (a measure of how often inventory is sold over time). It can help keep things from running out or being late, which improves customer service.
If a company has no other supply chain management modules, it can still use the inventory management app to handle shipping, buying, and sales orders. Larger businesses will need a version of this system that can track inventory in multiple places.
5. Taking Care of Orders
As orders come in and are delivered, an order control module keeps track of them. After a customer places an order, this part of the ERP sends it to the warehouse, distribution center, or shop and keeps track of its progress as it is prepared, filled, and sent to the customer. The order management section keeps orders from getting lost and increases the number of on-time deliveries. This keeps customers happy and reduces the cost of fast shipping, which is optional.
More advanced order management software can help a business determine which way to fulfill an order is the most cost-effective, such as a shop, a warehouse, or a third-party fulfillment partner, based on the buyer’s location and the available inventory.
6. Managing a Warehouse
Businesses that run their warehouses can get a quick return on their investment from a warehouse management tool. Based on how the warehouse is set up, this app can quickly and easily lead warehouse workers through their tasks, from putting away items when shipments come to picking, packing, and shipping. It can also help businesses plan their staffing needs based on how many orders they expect. Depending on what works best for a business, the warehouse management module can support different picking strategies, such as zone picking, batch picking, and wave picking. Some modules can also show workers the best way to pick items.
When the inventory management and order management apps are linked to the warehouse management tool, workers can quickly find the right items and send shipments out the door. In the end, faster shipping makes customers happier.
7. Managing the Supply Chain
A supply chain management module keeps track of all the steps that supplies, and things take as they move up and down the supply chain, from sub-suppliers to suppliers to manufacturers to distributors to retailers or consumers. It can also handle any materials or goods that are sent back to be refunded or replaced.
As was already said, supply chain management can include many different modules, such as purchasing, managing goods, making things, managing orders, and managing warehouses. But it could do things those sections can’t do independently.
8. CRM (Customer Relationship Management).
We keep customer and prospect data in the customer relationship management (CRM) section. This includes everything the company has said and done with a person, like the dates and times of calls and emails and what they have bought in the past. A CRM improves customer service because it makes it easy for employees to get all the data they need while working with a customer.
A lot of companies also use CRM to keep track of sales leads and chances. It can keep track of conversations with potential customers and suggest which customers should be contacted about certain deals or chances to cross-sell. More powerful CRM modules include advanced contact managers and reporting tools, and customer segmentation that lets you sell to specific groups of people more effectively.
9. Automation of Professional Services (Service Resource Management)
A service resource management module, which is another name for a professional services automation (PSA) module, helps a business plan and run projects. This section is often used by businesses that offer services. The app keeps track of the progress of projects, manages resources like people and money, and lets managers accept expenses and timesheets. All related papers are held in one place, which makes it easier for teams to work together. Along with that, the PSA module can make bills and send them to clients automatically based on rules about the payment cycle.
10. Managing the Workforce
A workforce management module is like a human resource management module, but it’s made for businesses with more hourly workers than paid workers. It can keep track of workers’ hours and attendance, as well as how productive they are and how often they miss work.
Payroll might also be part of the tool for managing employees. A payroll sub-module sends paychecks to employees on a set plan, with taxes already taken out, and takes care of reimbursement for business expenses. It can also give you data on KPIs like total overtime hours worked, payroll costs, and more.
11. Management of Human Resources
Human resource management (HRM) or human capital management (HCM) modules generally include all of a workforce management application’s features and some extra ones. HRM could be considered CRM for workers. This module is popular because it keeps detailed employee records and saves offer letters, performance reviews, and job descriptions. Not only does it keep track of hours worked, but it also keeps track of perks and paid time off (PTO).
The HRM section keeps much data on each employee across the company. This eliminates duplicate or incorrect data that many companies hold in different spreadsheets.
12. Online Shopping
Businesses that want to sell things online can get an ecommerce feature from some ERP providers. With this feature, businesses can quickly set up a business-to-business (B2B) or business-to-consumer (B2C) e-commerce site. The best commerce apps have easy tools for employees to use, so they can quickly add new items, change the look and feel of the website, and update product material like titles, descriptions, specs, images, and more.
If you connect the e-commerce app to other ERP apps, all the data about payments, orders, and assets goes from the e-commerce app to a shared database. Ensure all transactions are recorded, things that aren’t in stock are taken off the site, and orders are sent out on time.
13. Automation in Marketing
Some software companies have made a marketing automation tool, just like they did with e-commerce. A marketing module runs Marketing efforts through email, the web, social media, and text messages (SMS). It has advanced customer segmentation tools that ensure customers only get relevant messages and can automatically send emails based on marketing rules.
Whether it’s a separate solution or part of an ERP system, marketing automation software can give thorough reports on how campaigns are run that can be used to plan and spend money on marketing in the future. These apps bring in more leads, keep customers returning, and eventually make more sales.
How to Pick the Best ERP Modules for Your Company
If a business wants to buy ERP modules, it will depend on its business model, industry, ongoing problems, and other factors. However, most companies need a few modules to run their daily operations. A finance and accounting feature is necessary for every business to run, monitor its finances, and ensure its bills are paid. Runnieasier business with a switch that can give you financial data and do simple accounting chores is easier.
CRM is another module that would help most businesses. It’s not as important as finance and accounting, but almost every business, whether it sells goods or provides services, counts on some customer. In the same way, most companies with more than a few workers should buy the workforce management (HRM) module. People need to be paid on time, and companies need a central place to keep track of their information and how they’re doing in their careers.
A supply chain management module is useful for any business that makes, distributes, or sells goods. This includes almost all manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Most companies start with inventory and order management tools because they are important to day-to-day operations. Later, they may add manufacturing, warehouse management, and purchasing solutions.
With a project management tool, service businesses like consultancies, agencies, and repair and maintenance shops could see a quick return on their investment. It handles complicated billing tasks that take a lot of time, making planning project resources easier.
Some people wouldn’t include commerce and marketing automation as ERP software, but many businesses need them to get new customers and keep their existing ones. This is especially true now that the Internet is such a big source of new business. There are many marketing automation and commerce solutions from companies that aren’t ERP providers. Still, the ones from your ERP provider offer a tighter, more reliable integration and may share a common user interface that makes it easier for workers to learn and use.
Buying and setting up an ERP platform was scary and overwhelming when I started. But if you start with the right ERP system for your business, you can begin immediately and add to it as you grow. The best ERP features for your business are the ones that meet your needs now and can be expanded to help you handle the challenges and chances that come with growth.
FAQs of ERP Modules
What are the parts of ERP?
ERP modules are pieces of software that are designed to do specific tasks and roles for a business. The central database of the ERP system connects all parts, so there is only one source of correct data. This also makes it easy for systems that do different things, like finance and inventory management, to share information and work together to complete bigger jobs.
What is ERP, and what kinds are there?
Enterprise resource planning, or ERP, is a platform that many businesses use to run their day-to-day processes. The ERP is linked to systems that handle important tasks like banking, supply chain, HR, customer relationship management (CRM), project management, and more.
ERP can be delivered in several ways, such as in the cloud, on-premises, or as a mix. An on-premises system needs servers that the company owns, while a cloud system runs on servers that are far away and may be handled by the software vendor. A hybrid approach takes parts of both on-premises and cloud ERP systems and uses them together.
What features does every ERP system have to have?
Which ERP modules a company needs depends on its business needs. However, most companies start with a finance module to handle accounting tasks, keep track of all financial data, and generate important reports. A CRM is another popular module because every business needs to keep track of its users. Companies that sell goods usually need tools for managing inventory, orders, and other parts of the supply chain. Companies that provide services typically require a professional services automation application.
Best cloud ERP software solution

About Us
ERP software and systems are designed and implemented by Multi-Techno, a registered company. By combining data from financials, sales, CRM, inventories, and operations, businesses can increase productivity, make better decisions, and increase profitability with the aid of our ERP System, a single, integrated software platform.
Quick Links
Contact Us
Office # 100, 101 Second Floor Kohinoor 1, Faisalabad, Pakistan
